Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is generally treated without surgery. Surgery can only be considered when:
- After 5 years of non-surgical treatment.
- Severe symptoms causing severe pain
- If there is a risk or damage of median nerve
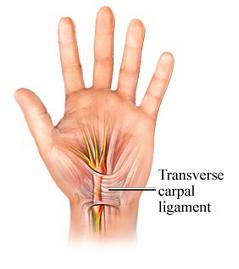
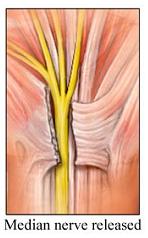
This reduces the pressure on the median nerve, which is done by cutting the ligament which forms over the Carpal Tunnel.
Open Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
In this Open Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery, Doctor can have a good view of inner tissues and even the Transverse Carpal Tunnel ligaments, which allows the surgeon to easy cutting of the tissue. This Treatment method need an incision in the palm and wrist, which disturbs more tissues in the hand, there by requiring a longer period to recover. Another draw back of this surgery is that it leaves a larger scar on the hand than the Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Syndrome surgery.
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
In this Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery, doctors need only a small incision at the wrist which is a single-portal technique or a small incision at the wrist and palm which is a two-portal technique. This method disturbs lesser tissues when compared to the open Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery and this method even leaves a smaller scar on the wrist.
Carpal Tunnel Surgery Methods:
- Open Release,
- Mini Open Release,
- Endoscopy,
- Percutaneous Balloon Carpal Tunnel-Plastry.
A number of experts believe that Carpal Tunnel Surgery is performed frequently and that CTS patients should opt for the non-surgical methods of treatment before going for a Carpal Tunnel Surgery and some experts argue that often the condition is progressive and will worsen over time without the Carpal Tunnel Surgery, which generally brings good results.
One study indicated performing Carpal Tunnel Surgery within three years of the diagnosis of CTS is more successful than waiting for long periods as actually waiting for long period can reduce the benefits of the surgery. The Electrodiagnostic tests for nerve conduction might be more helpful in determining who would most like to get benefited from the this type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery.
The results suggested that workers who had significantly slow nerve conduction and other abnormal results showed the most improvement after Carpal Tunnel Surgery and those who had normal or near-normal nerve conduction results before surgery were least likely to get benefited from the Carpal Tunnel Surgery. As said by a study patient who had less preoperative muscle weakness and whose symptoms were worse at night most likely to be satisfied with the Carpal Tunnel Surgery.
Patients suffering from CTS, which is an outcome of nerve damage due to medical conditions, like the diabetes, hypothyroidism, or rheumatoid arthritis, appear to have the same outcome as those without such conditions and so such disorders should not prevent the Carpal Tunnel Surgery.
It is generally Carpal Tunnel Surgery is recommended if symptoms of CTS continue to exist for four to six months and if muscles begin to atrophy in the base of the palm. The surgical procedure does not always cure all patients because it permanently cuts the carpal ligament, which might lead to loss of wrist strength.
Open Release Surgery:
Carpal Tunnel Surgery generally is an open surgical procedure performed in an outpatient facility. A local anesthetic is injected either into the hand or higher up the arm and wrist. A two-inch incision in made in the palm by the surgeon and he cuts the carpal ligament free from the underlying median nerve by which the ligament is literally released and therefore the pressure on the median nerve is relieved.
The risk of complications with this surgery is less than one percent. Although other techniques are being developed, this procedure is still the most cost effective. Carpal tunnel release is the most commonly performed hand surgery, with more than 100,000 procedures each year.
Mini-Open Release Surgery:
Mini open release technique is the more recent variation of Carpal Tunnel Surgery, in which an incision that is only about an inch and a half. With the help of only a local anesthetic the mini open release surgery can be performed in the doctor’s office itself and it takes just about 12 minutes.
A study on the results reported that there is no loss of finger mobility, recurrence of CTS after a year, and no infection, or no injury to the median nerve but it is more expensive than standard open release surgery.
Endoscopy
Endoscopy type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome is a less engaged procedure when compared to the standard open release. One or two 1/2-inch incisions are made in the wrist and palm, and one or two endoscopespencil-thin tubes are inserted and into these lighted tubes a tiny camera and a knife are inserted. The surgeon cuts the ligament to free the compressed median nerve while observing the underside of the carpal ligament on a screen.
his type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery doesn’t leave a surgical scar to the patients and often they can return to work within half the time as taken by the standard open surgery type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery.A 1998 analysis report, reported that success rates of this type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery are average about 96%; complication rates are 2.7%; and failure rates are 2.6%. In one study, 98% of patients after having Carpal Tunnel Surgery experienced relief of numbness and weakness and in 90% pain was reduced. Only 12% of patients required more than two doses of pain relievers after the Carpal Tunnel Surgery.
In some studies, patients had better grip strength after Endoscopy Carpal Tunnel Surgery rather than after standard release type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery, and, in many studies, patients reported less pain and returned to normal activities earlier than those who had the open release procedure of Carpal Tunnel Surgery. Complications, including tingling or loss of sensation in the fingers, increase with surgeons who are less experienced. Usually, such complications of Carpal Tunnel Surgery are temporary.
As surgeons gain more experience with this procedure, studies are now reporting similar success and complications rates to standard Carpal Tunnel Surgery.
Some experts believe that there may be a higher recurrence rate of CTS with endoscopy type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery because the view of the hand is limited during this procedure and surgeons may not see complicating conditions that may require treatment where as in the open release procedure type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery, the surgeon has a full view of the structures in the hand.
Post- Carpal Tunnel Surgery conditions for some patients who had Carpal Tunnel Surgery relieve CTS symptoms of numbness and tingling immediately and a study reported that within six weeks the grip and pinch strengths exceeded preoperative status.
A study reported that the peak improvements of Carpal Tunnel Surgery might take long time of an average of almost 10 months. There can be complications of Carpal Tunnel Surgery, like the pain, scarring, infection, nerve damage and stiffness after the Carpal Tunnel Surgery. Patients may experience some scar pain for years with open release type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery and the incision site may remain sore for months.
People who have the Carpal Tunnel Surgery on both the hands are completely incapacitated for about two weeks and must have someone to help them at home. The symptoms may return after returning to strenuous work right after Carpal Tunnel Surgery, for this reason generally the patients stay out of work for at least month and sometimes even much longer, depending upon the severity of the condition and type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery.
Physical therapy is very important to help in rebuilding the wrist strength. To restore circulation, muscle strength, and joint flexibility in the hand and wrist, hand exercises are helpful.
The long-term outcome of the Carpal Tunnel Surgery has been conducted by few studies for patients after they returned to work. A 18-month study reported that over 70% of those who had the open release type os Carpal Tunnel Surgery experienced improvement in at least one of three symptoms (pain, numbness, and tingling) and only about half experienced reduction of pain, numbness and tingling sensation and over 90% had normal grip and pinch strength.
Another study, reported that after five years of Carpal Tunnel Surgery, 30% of patients experienced some scar pain and poor to fair strength and in 57% some symptoms returned, especially the pain and certain people always experienced residual numbness in the fingertips. In spite of all these negative outcomes, 87% of the patients in the study reported that, generally their outcomes were good to excellent.
The people those who are involved with heavy manual labor, particularly those working with vibrating tools and the elderly people, those who experienced very severe symptoms before Carpal Tunnel Surgery appear to have a poorer outcome than any others.
A five-year study had found that there appears slow improvement in people who had been working at heavy labor and also that they had to stay out longer, but responses after five years after Carpal Tunnel Surgery, they did not differ among occupational groups.
Some studies indicated that however, only slightly more than half the people who used vibrating hand-held tools were symptom-free for just three years after their Carpal Tunnel Surgery because between 10% and a third of patients lose some of their wrist strength with both open release and endoscopy type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery, patients may not be able to perform well in the jobs requiring high amounts of force to the hand and wrist.
Such workers may also have problems in other parts of the upper body, including elbows and shoulders that are not resolved with Carpal Tunnel Surgery and can exist. Some studies have also indicated that between 10% and 15% of patients have changed their jobs after the Carpal Tunnel Surgery.
Percutaneous Balloon Carpal Tunnel-Plasty:
In this type of Carpal Tunnel Surgery ie., Percutaneous balloon carpal tunnel-plasty relieve of CTS is done without cutting the carpal ligament. The doctor inserts a balloon through a 1/4-inch incision in the base of the palm, through a catheter under the ligament, and after that he inflates the balloon using saline solution to stretch the ligament and by this he makes the median nerve free of pressure.
A small study, reported that all of the patients who had this Percutaneous balloon carpal tunnel-plasty Carpal Tunnel Surgery reported relief of symptoms with no postoperative complications and most of them were back to work within a period of two weeks. This experimental technique of Carpal Tunnel Surgery is not yet widely available.